Beyond the Buzz: A Comprehensive Look at THC and Its Cousins

What is THC: The Basics
As cannabis laws evolve, many people are asking: what is THC? Simply put, THC (delta-9-tetrahydrocannabinol) is the main compound in the cannabis plant that causes the "high" feeling.
Here’s a quick overview of THC:
- Psychoactive: THC is the primary psychoactive ingredient in cannabis, affecting your brain and mood.
- Source: It comes from the Cannabis sativa plant.
- Effects: When consumed, THC binds with brain receptors, leading to euphoria, relaxation, and altered perception.
- Legality: The legal status of THC varies widely. Some states allow it for medical or recreational use, while it remains federally illegal in the U.S.
THC is one of many cannabinoids in the cannabis plant. While known for its psychoactive effects, it also has potential medical uses, which we'll explore in this guide. The cannabis plant has also evolved, with average THC strength jumping from ~4% in the mid-1990s to over 15% today, making modern products much more potent.
I'm Max Shemesh, Owner & CEO of Zaleaf. My passion is delivering high-quality cannabinoid products. I've dedicated my career to understanding what is THC and how it interacts with the body to ensure our formulations meet the highest standards.

Find more about what is thc:
What is THC and How Does It Work?
We know what is THC causes the "high" from cannabis, but how does it work? THC interacts with our body's endocannabinoid system (ECS), acting like a key that open ups a range of effects in our brain and body.
The Chemical Makeup of THC
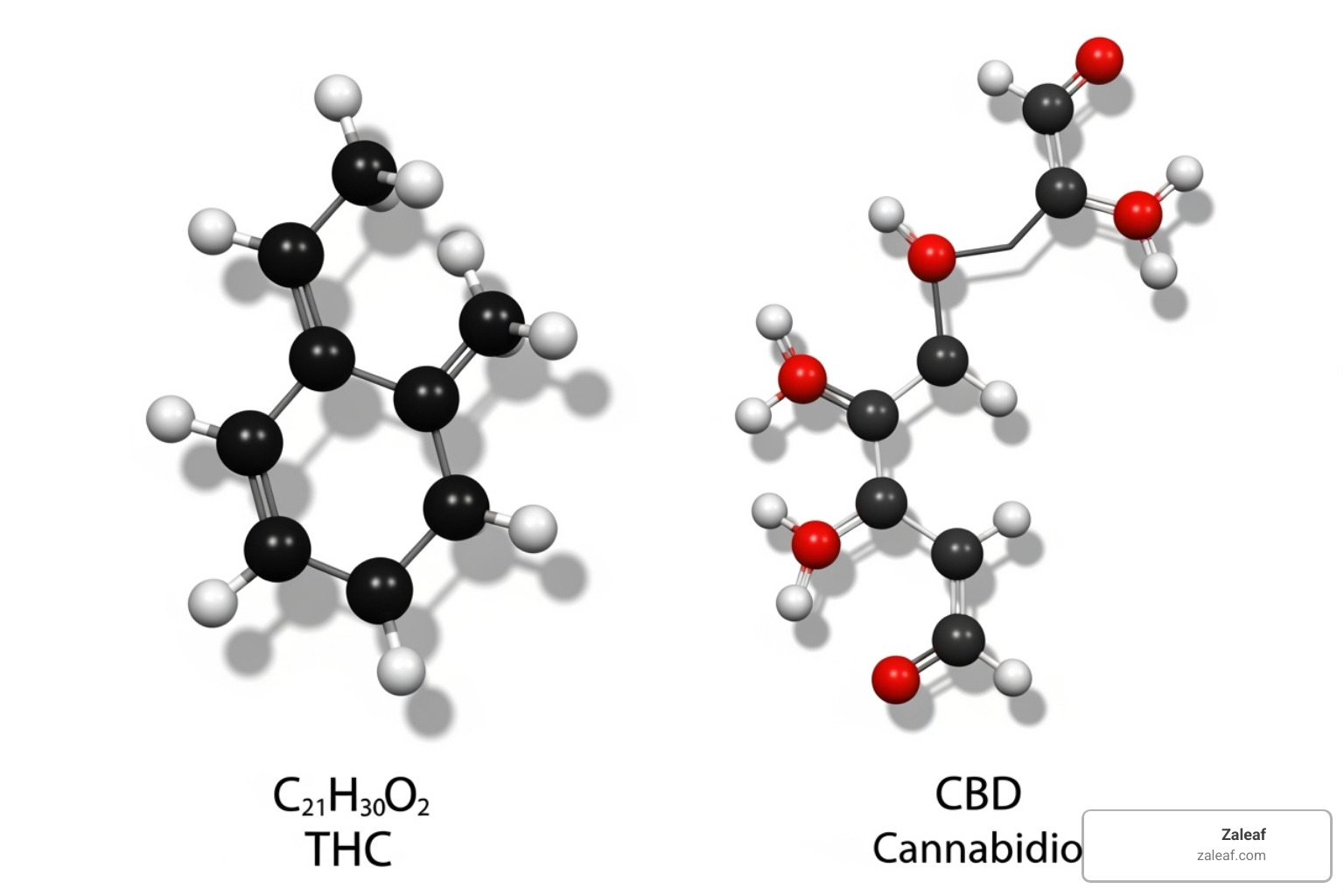
THC's chemical formula is C21H30O2. This specific arrangement of atoms gives delta-9-tetrahydrocannabinol its unique properties. THC also has isomers, or "cousins," like Delta-8-THC and Delta-10-THC. These compounds have the same atoms but a slightly different structure, resulting in different effects and potencies.
In the raw cannabis plant, THC exists as non-psychoactive tetrahydrocannabinolic acid (THCA). It must be heated—a process called decarboxylation—to become the active THC we know. This is why eating raw cannabis won't get you high.
What is THC's role in the endocannabinoid system?
Our bodies have a master regulator called the endocannabinoid system (ECS), which helps balance functions like mood, appetite, pain, and memory. The ECS has two main receptor types: CB1 receptors (mostly in the brain and central nervous system) and CB2 receptors (found in immune cells and other organs).
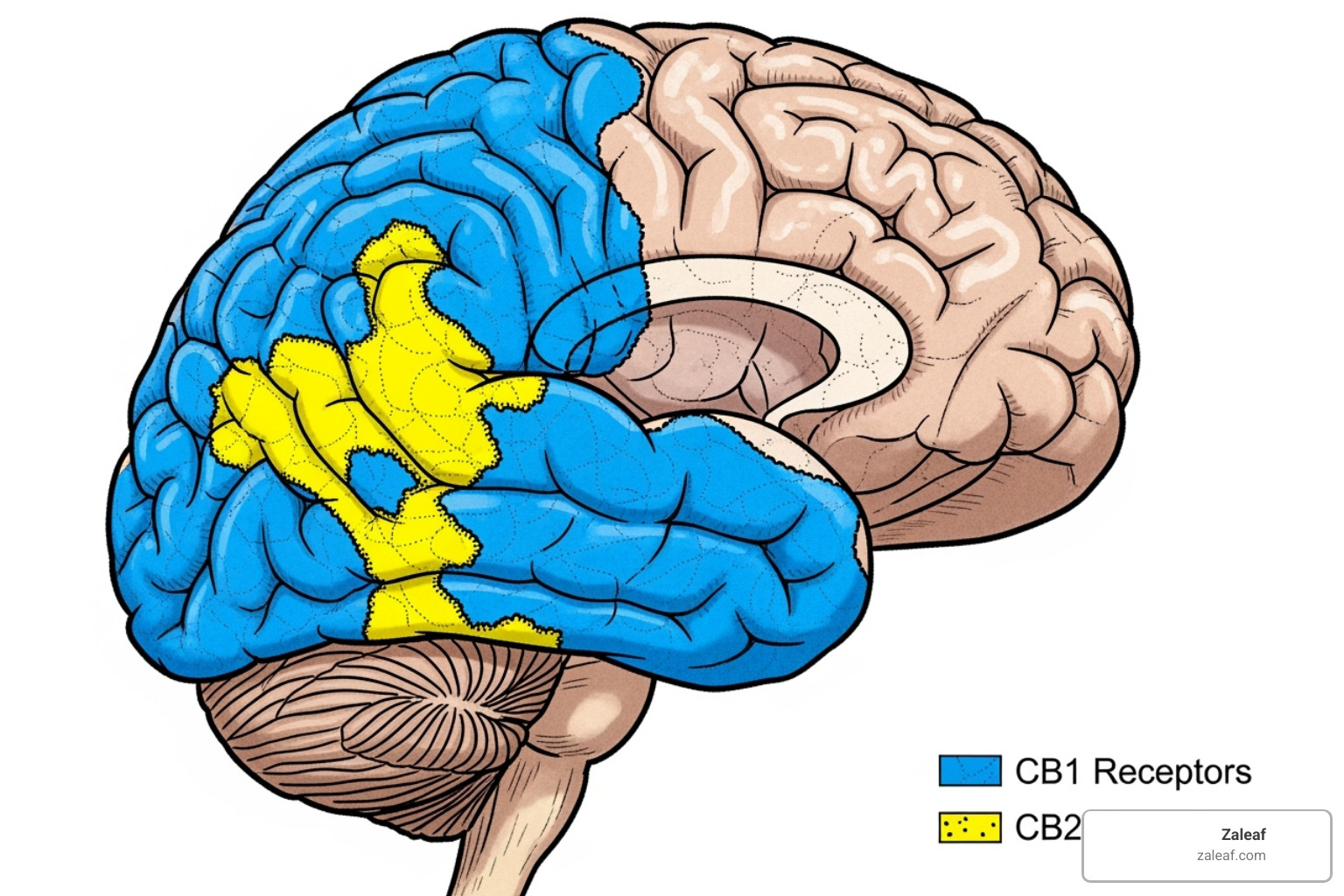
THC mimics our natural endocannabinoids, particularly anandamide (the "bliss molecule"). It binds perfectly to CB1 receptors in the brain, triggering a release of dopamine. This causes the feelings of euphoria, relaxation, and altered perception known as the cannabis "high." This interaction also temporarily affects concentration, judgment, and memory, highlighting the importance of understanding THC's mechanisms. For a deeper dive, you can explore scientific research on THC's mechanism.
The Effects of THC: Benefits vs. Risks
Understanding what is THC involves weighing its benefits against its risks. It's a powerful compound that can be medically useful but also has potential downsides if misused.
Potential Medical Benefits
The medical community is increasingly recognizing THC's potential for treating various conditions.
- Pain relief: One of THC's most recognized benefits is pain relief, especially for chronic nerve pain from conditions like multiple sclerosis.
- Nausea and vomiting: THC is highly effective against nausea from chemotherapy. The FDA has approved synthetic THC versions (dronabinol, nabilone) for this purpose.
- Appetite stimulation: The "munchies" effect is medically valuable for patients with conditions like AIDS or anorexia that cause appetite loss.
- Insomnia and Muscle Spasticity: Many people use THC for insomnia. It's also being researched for reducing muscle spasticity in conditions like epilepsy and Parkinson's disease.
Research continues into THC's use for glaucoma, Alzheimer's, Crohn's disease, and PTSD. You can find more information on FDA-approved THC medications in scientific literature.
Potential Risks and Side Effects
However, understanding what is THC also means acknowledging its risks, especially at high doses or with frequent use.
Immediate side effects can include impaired judgment and memory, anxiety and paranoia, drowsiness, and an increased heart rate. Ironically, while it often treats nausea, it can sometimes cause nausea and vomiting.
Long-term use of high-potency THC is linked to mental health concerns, including hallucinations, delusions, and increased psychosis risk, especially for adolescents. While controversial, amotivational syndrome (reduced motivation) is linked to heavy use. Cannabis use disorder is also a reality, with about 9% of users potentially developing dependence. Smoking cannabis also carries respiratory problems similar to tobacco use.
The takeaway is that THC offers real benefits but isn't without risks. Responsible use requires understanding both sides and making informed choices.
THC vs. CBD: A Tale of Two Cannabinoids
Beyond THC, the cannabis plant contains another major cannabinoid: CBD (Cannabidiol). Though they come from the same Cannabis sativa plant, THC and CBD have very different properties and effects.
Key Differences in Effects and Benefits
The primary difference is psychoactivity. What is THC known for? The euphoric "high." CBD, in contrast, is non-psychoactive and won't cause intoxication.
This difference is due to their molecular structure. Although they share the same chemical formula (C21H30O2), their atoms are arranged differently. THC binds strongly with the brain's CB1 receptors, causing the high. CBD has a weak affinity for CB1 receptors and works through other pathways to provide benefits like pain and inflammation relief without intoxication. CBD may even counteract some of THC's negative effects, like anxiety.
Here’s a quick comparison:
| Feature | THC | CBD |
|---|---|---|
| Psychoactivity | Yes, produces a "high" or euphoric sensation. | No, does not produce a "high." It's non-intoxicating. |
| Primary Interaction | Binds strongly to CB1 receptors in the brain. | Binds weakly to CB1 receptors; interacts with other receptors and enzymes in the ECS. |
| Medical Uses | Nausea and vomiting (chemotherapy), appetite stimulation (AIDS/anorexia), pain relief, muscle spasticity, insomnia. FDA-approved synthetic forms exist. | Anxiety, inflammation, nerve-related pain, epilepsy (FDA-approved Epidiolex for rare forms). Research ongoing for many other conditions. |
| Side Effects | Impaired judgment, anxiety, paranoia, increased heart rate, memory issues, drowsiness, potential long-term psychiatric effects (especially high potency/adolescents), amotivational syndrome. | Nausea, diarrhea, upset stomach, tiredness, lightheadedness, crankiness, low blood pressure. Generally well-tolerated with fewer severe side effects than THC. |
| Legality | Federally illegal in the US (Schedule 1), but legal for medical or recreational use in many states. Varies significantly by region. | Federally legal in the US if hemp-derived (less than 0.3% THC) due to the 2018 Farm Bill. State laws vary. Marijuana-derived CBD is federally illegal. Often unregulated by FDA, leading to purity/labeling concerns. |
| Drug Testing | Most standard drug tests look for THC metabolites, so THC use will likely result in a positive test. | Typically does not cause a positive result for THC, but full-spectrum CBD products may contain trace THC (under 0.3%), potentially leading to a false positive if consumed in large amounts or if products are mislabeled. |
Legality and Sourcing
The legal landscape for THC and CBD is complex, with conflicts between federal and state laws. The key distinction lies in the legal definitions of "marijuana" and "hemp."
Federally, delta-9-THC from marijuana is a Schedule I controlled substance. However, the 2018 Farm Bill legalized hemp, defined as any Cannabis sativa plant with less than 0.3% delta-9-THC. Products derived from hemp are federally legal. Zaleaf products are 100% legal as they adhere to these federal guidelines.
Despite federal law, many states have legalized medical or recreational marijuana. This means what is THC's legal status can change dramatically from one state to another. Due to this patchwork of laws, it's crucial to check your local regulations. You can use resources like state-by-state cannabis laws to stay informed. Zaleaf ensures all products are legal in your area before shipping, so you can order with confidence.
Navigating the World of THC: Products, Potency, and Legality
Once you understand what is THC, you'll find a vast world of products beyond traditional dried flower. From edibles to vapes, each consumption method offers a unique experience in terms of onset, duration, and effects. Choosing the right product is key to a positive experience.
Common Forms of THC
- Smoking flower: The traditional method. Effects are felt within minutes and last 2-4 hours, allowing for easy dose control.
- Vaping: Heats cannabis flower or concentrates without burning, seen as a cleaner alternative to smoking. Onset is rapid, and concentrates can be very potent.
- Edibles: Includes THC-infused gummies, chocolates, and drinks. Effects are delayed (30-120 minutes) and long-lasting (4-8+ hours). The golden rule is to start with a low dose and be patient.
- Tinctures: Liquid extracts dropped under the tongue for relatively fast absorption (15-45 minutes). Effects last several hours, and dosing is precise.
- Topicals: THC-infused creams and balms applied to the skin for localized relief. They are non-psychoactive as the THC doesn't typically enter the bloodstream.
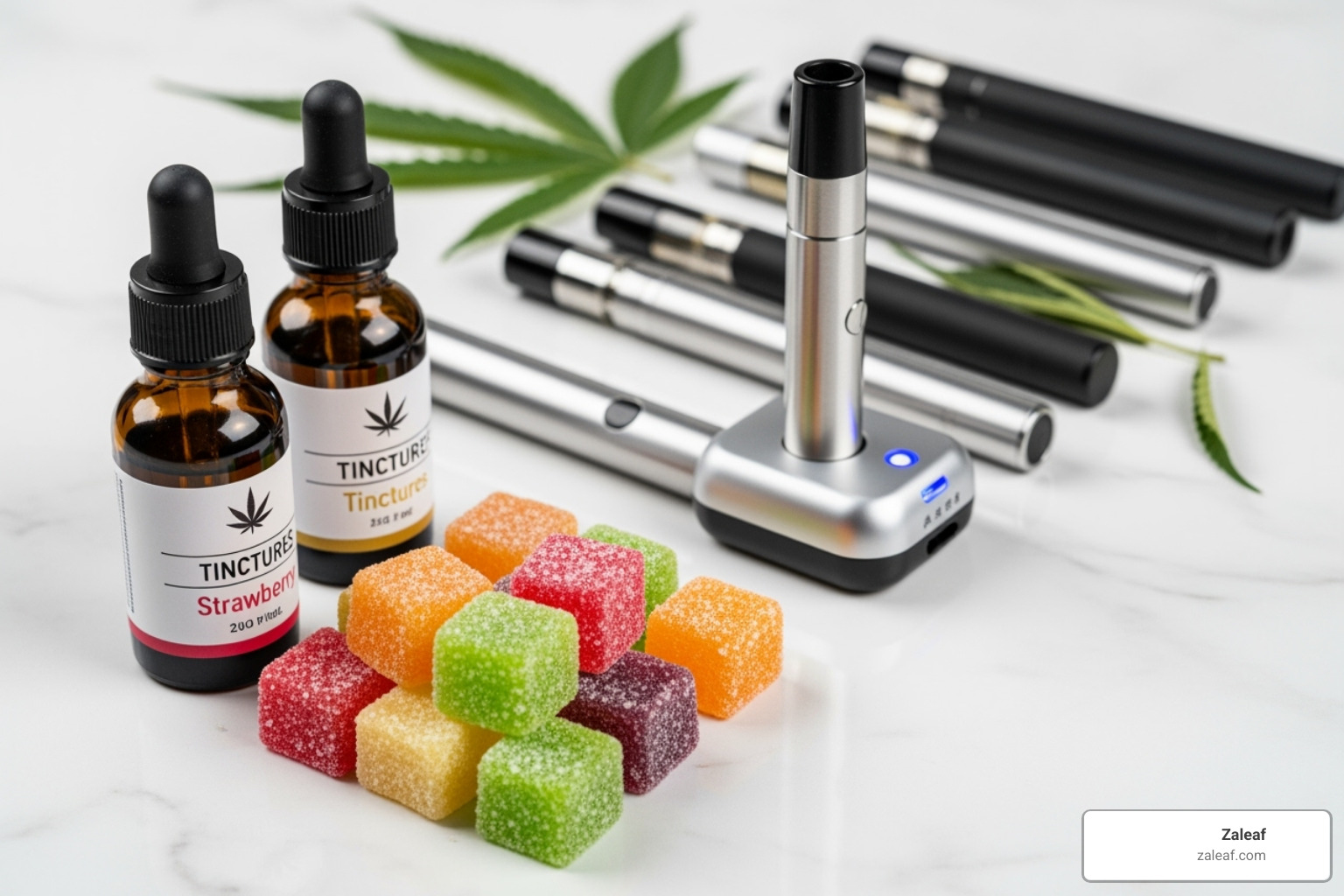

At Zaleaf, we craft products with specific cannabinoid and terpene profiles to target moods like relaxation or focus. Explore different types of cannabinoid products to find your perfect match.
THC Potency and What is THC's legal status?
Today's cannabis is much stronger than in the past. In the mid-1990s, average THC content was about 4%; now it's over 15%. This increased potency makes understanding your dose crucial. All Zaleaf products are third-party lab tested, so you know exactly what you're getting.
As mentioned, what is THC's legal status is complicated. Federally, it's a Schedule I substance, but most states have their own laws, with 38 allowing medical use and 24 allowing recreational use. The 2018 Farm Bill legalized hemp (cannabis with <0.3% delta-9-THC), making hemp-derived products federally legal.
This is why Zaleaf products are 100% legal nationwide. We adhere to the 0.3% Delta-9 THC limit, so no medical card is needed. We offer fast, discreet shipping for a simplified legal cannabis experience. The legal landscape is always changing, so it's important to stay informed about local and federal laws.
Frequently Asked Questions about THC
Here are answers to some common questions about what is THC.
How long does THC stay in your system?
This is a common question, but the answer is complex. Detection windows depend on factors like frequency of use, individual metabolism, and body fat percentage, as THC is stored in body fat.
The detection window also depends on the test type:
- Urine tests: 3 to 30+ days
- Blood tests: A few hours to a few days
- Hair tests: Up to 90 days
Note: While Zaleaf products are federally legal, our full-spectrum options contain trace amounts of THC (<0.3%). This could potentially be detected in sensitive drug tests. Please consider your personal situation.
Can you build a tolerance to THC?
Yes, tolerance is common. With regular use, the brain's CB1 receptors can become less sensitive (downregulation), leading to diminishing effects. This often results in increased consumption to achieve the same feeling. The good news is that tolerance breaks (abstaining for a few days or weeks) can help reset your system and restore receptor sensitivity.
What is the difference between Delta-8 and Delta-9 THC?
Delta-8 THC has become popular as a legal option with milder effects than traditional Delta-9 THC. Their chemical structures are nearly identical, but a small difference makes Delta-8-THC about half as potent as Delta-9-THC. Many users report a clearer, less anxious high from Delta-8.
Regarding sourcing, most Delta-8 is created by converting CBD from legal hemp. Legally, Delta-8 from hemp is often considered federally legal under the 2018 Farm Bill, but some states have banned it, so always check local laws. Zaleaf's Delta-8 offerings provide a legal way to explore THC's benefits with confidence.
Conclusion
We've explored what is THC (delta-9-tetrahydrocannabinol), from its chemical structure to its interaction with our brain's CB1 receptors. This single molecule has profound effects on the body and mind.
THC is complex. It offers medical benefits like chronic pain relief and appetite stimulation, but also carries risks, especially given that modern cannabis is much more potent. The contrast between THC and CBD shows the nuance of cannabis: THC is psychoactive, while CBD offers benefits without intoxication.
Navigating the legal landscape is crucial. Understanding what is THC's legal status, from federal law to state rules, is key. At Zaleaf, we simplify this by offering 100% legal cannabis products that comply with federal guidelines.
Whether you're interested in Delta-8, drug testing windows, or tolerance, knowledge is power in the rapidly evolving world of cannabis. Zaleaf makes this world accessible and safe. We create mood-specific effects with improved cannabinoid profiles, ensure quality with 3rd party testing, and offer fast, discrete shipping with no ID or medical card required.
As our understanding of what is THC grows, so does our ability to use it responsibly. By staying informed and choosing a reputable source, you can confidently explore the benefits of cannabis.
Ready to find how legal cannabis products can improve your well-being? Find mood-specific legal cannabis products at Zaleaf today and experience the difference that quality and expertise make.

